ISDN Technology Overview
ISDN Concepts: Integrated Voice and Data
ISDN stands for Integrated Services Digital Network, which provides many voice and data communication features.
The basic ISDN service provides two 64,000 bits per second "B" channels for voice or data communications. Each "B" channel can support circuit-switched or packet-switched data services. There is also one "D" channel, at 16,000 bits per second, for network signalling and packet-switched data service. The combination is often referred to as "2B+D," or the Basic Rate Interface (BRI).
Voice Features
The voice features of an ISDN telephone have several advantages:
- They allow your telephone to handle multiple calls simultaneously, receiving calls while keeping others on hold.
- They also permit a call coming in to a single directory number to ring more than one physical telephone. This facilitates call handling within a group.
- They provide easy-to-use access to powerful features such as call conferencing and call transfer, to enhance the productivity of your telephone use.
Data Features
The data features of an ISDN telephone include the following features:
- Communicate on the D-channel using packet switching with an asynchronous RS-232C terminal at speeds up to 19,200 bits per second.
- Communicate on the B-channel using packet switching with an asynchronous RS-232C terminal at speeds up to 19,200 bits per second.
In order to do any data communications, your telephone needs to have a data module installed, and to have the supporting network data features assigned to it.
Multipoint Configurations
Today, most telephone connections are point-to-point. Each telephone in a point-to-point configuration requires a separate line into your building. However, many service providers now offer multipoint configurations as a subscription option. ISDN supports both point-to-point and multipoint.
In a multipoint configuration, up to eight devices (digital sets and/or terminal adapters) can be connected to a single line. For example, your company may connect two digital sets and two terminal adapters to a single line, particularly if the terminal adapters us the D-channel packet switching. The two digital set users could use the two B-channels, and the terminal adapters could use packet switching for data calls on the D-channel.
ISDN Glossary
- BRI (Basic Rate Interface) = 2B+D, Two 64Kb/s B-Channels that can carry voice or data and the 16Kb/s D-Channel used for packet data and network control signaling.
- "U" Interface = 2 wire ISDN interface that generally connects the customer location to the central office.
- "T" or "S/T" Interface = 4 wire ISDN interface usually behind the NT1. Tip(1) Ring(1) and Tip(2) Ring(2) have PS1 power overlaid on each conductor.
- NT1 (Network Termination) = CPE device that terminates layer 1 of the "U" and "T" interfaces. It converts the physical and electronical signals from the two wire "U" interface to the 4 wire "S/T' interface. NT1 units (2B1Q/ANSI) are universal in that they can be used with any brand ISDN Telephone.
- Local Power Supply = 40V - 48V power supply. Plugs into wall and supports one NT1 and one to two telephones(ie: 353A, MSP1, and 1215A).
- Bulk Power Supply = Power supply unit centrally located at the Main Distribution Frame(MDF) or a sub closet. These units support 1 to 96 telephones depending on the manufacturer and model(ie. 1145B Kit).
- PS2 Power = -48V and ground on pins 7 and 8 provide necessary power to the NT1 and ISDN Telephone.
- PS1 Power = Power overlaid on pins 1 and 2 that will operate the telephone in the event that PS2 Power is lost.
- API Data = ISDN Telephone that is capable of sending and receiving modem AT commands from the D-Channel. This allows PCs to interface with a serial cable and place/answer calls, provide caller ID for screen pop applications, and store additional numbers for memory calling.
Point to Point

One ISDN Telephone per ISDN Circuit.
Multipoint or "Passive Bus"
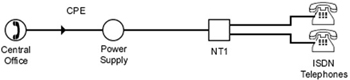
Multipoint allows more than one ISDN Telephone per Unit. Up to 8 ISDN Telephones can be connected sharing the same ISDN Circuit and NT1 Unit. The most common application for multipoint is when two ISDN Telephones share one NT1 and circuit, each receiving one dedicated B-Channel. This allows the end user to reduce their line cost by half.
Voice and Data
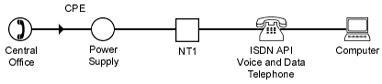
1 B-Channel for Voice and 1 B-Channel for Data.
|




